great article from Ben Greenfield and Dr. Jack Kruse that I wanted to share.
Two Stunning But Little-Known Ways To Fix Your Body: Unlocking The Power Of Light & Cold
The Effects of Light in Biology
Let’s begin with the stuff pouring out of the screen you’re reading this on right now: light.
As you can learn in the podcast “How To Use Low Level Light Therapy And Intranasal Light Therapy For Athletic Performance, Cognitive Enhancement & More” light energy is, according to quantum mechanics, composed of photons or packets of energy. The energy of a single photon depends on its wavelength. Therefore, the energy in a “dose” of light depends on the number of photons and on their wavelength or color (for example, blue photons have more energy than green photons that have more energy than red, that have more energy than near infrared (IR), etc.)
The shorter the wavelength of light, the greater the energy transferred to the electron. Ultraviolet (UV) is shorter than IR, for example, and that means UV photons carry more energy than IR ones. That’s why you can hang out in an IR sauna all day long and just sweat, but if you hang out in the UV photon light of the sun all day long, you may get a bit of radiation on your skin that we call a sunburn. This is because the intensity of the light determines how many photons strike any given surface and how many electrons are, thus, affected. The higher the intensity of light, the greater the number of photons and therefore, the greater the amount of energy transferred to the electrons.
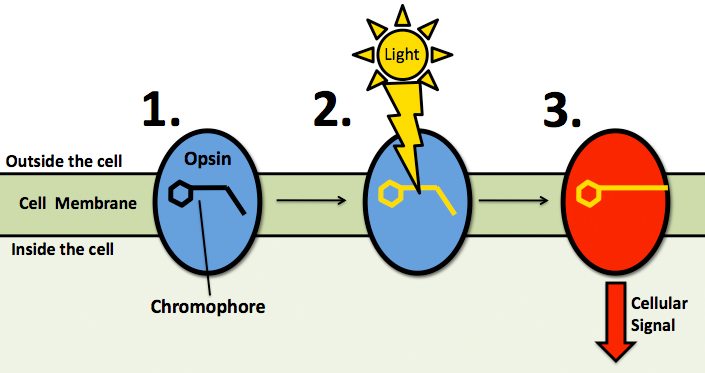
Photons that are delivered into living tissue can either be absorbed or scattered. Photons that are absorbed interact with a chromophore located within the tissue, such as is the case with the eyes (and as illustrated below). A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color arises when a molecule absorbs certain wavelengths of visible light and transmits or reflects others.
Light reception in animals is mediated by opsin visual pigments. Opsins are receptor proteins that are attached to a light-sensitive chromophore, which is made by your body from vitamin A (yup – that’s why vitamin A-rich carrots are beneficial for your eyesight). Chromophores change shape when they absorb a photon of light. This activates the opsin that it is bound to and causes it to send a cellular signal which can be interpreted by the nervous system.
The effects of light in biology, specifically termed “photobiomodulation”, were discovered over 40 years ago and have since been studied at institutions such as Harvard, NASA and the Department of Defense. Most of the evidence for photobiomodulation has focused on light therapy that improves tissue repair (skin wounds, muscle, tendon, bone, nerves), reduces inflammation and reduces pain wherever the beam is applied. (PubMed refs)
Photobiomodulation has a photochemical effect, much like photosynthesis in plants. One of the main mechanisms of action occurs in your mitochondria, the cellular power plants inside nearly every cell of our bodies. Photobiomodulation studies have provided sufficient empirical evidence of the value of light in medicine. The effect depends on the application of the correct wavelength and density of light, delivered to the target tissues for an appropriate period of time.
OK. Hold up a sec.
Smoke pouring out your ears yet from this information dump?
All you’ve basically learned so far is that just like a plant can absorb light to make energy, your body can absorb light to make energy.
Yes, you are kind of like a plant.
Let’s dive even deeper, shall we?
———————–
How Light Affects Your Blood
Let’s next imagine what would happen if your blood was exposed to a daily influx of therapeutic light…
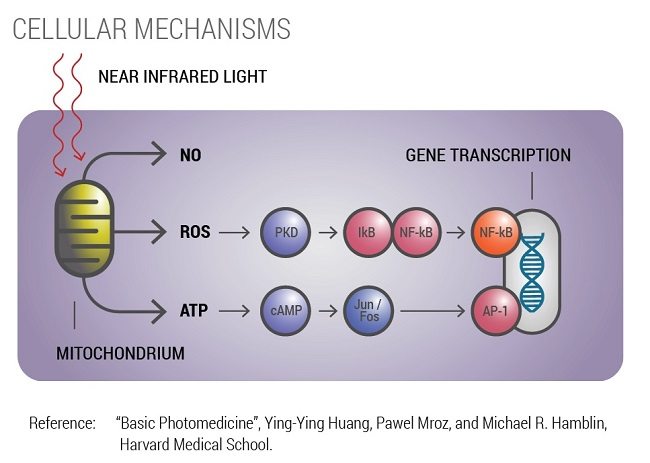
According to the scientific literature, light acts at the cellular level by stimulating cells to generate more energy and utilize oxygen more effectively. Within certain blood-based cells exist mitochondria, which produce cellular energy in the form of a molecule called adenosine triphosphate or ATP for short.
An enzyme in mitochondria known as cytochrome c-oxidase (CCO) utilizes light photons to increase ATP and reduce oxidative stress. A cascade of mitochondrial and intracellular downstream effects lead to improved tissue repair and reduced inflammation.This process also creates mild oxidants (ROS) that lead to both cellular repair, healing and gene transcription. (Pubmed references here).
In multiple studies conducted in Russia, China, Brazil, and Germany, specific frequencies and intensities of light delivered directly into the blood included improvements in lipid levels and cholesterol, improved blood sugar levels, better clotting, reduction of arthritic pain and fibromyalgia symptoms, and even increased immunity.
So light hits your blood, decreases inflammation and allows for enhanced cellular energy production. And that, my friend, is why you feel so, so good when you go for a walk in the sunshine. And that’s also why most plants die without light.
Yep, remember, you are very much like a plant.
Now let’s look at the implications of this for performance…
—————————–
Light to Enhance Athletic Performance
About the worst thing you can do for physical or mental performance is to spend your day indoors, without light – even if it’s in a gym or training facility. And here’s why…
In sports medicine in particular, photobiomodulation has demonstrated increased exercise capacity and longer exercise times, as well as improved biomarkers (including reduced Lactate, Creatine Kinase, and CRP) after exercise in people treated with red and infrared light. It has also been reported to release certain brain compounds that positively affect mood and sleep.
The Italian researchers Raggi and Vallesi performed a first study in athletes for investigation the effect of blood irradiation on strength and endurance. The data were published in the journal “Schmerz & Aupunktur” in Germany in 2008. In this study, athletes showed remarkable benefits, increasing their exercise performance by over 20% in multiple exercise categories from just 10 days of blood irradiation.
What’s more interesting is that the effects lasted for 16 weeks after the end of the treatment! The researchers hypothesized that this duration had to do with red blood cells’ mean lifetime: 12-15 weeks.
Several other studies can be found in the literature that are of significance in sports medicine. First, a Polish study that demonstrated higher exercise capacity, longer exercise time and longer distance of a 6 minute walk test, in 39 coronary artery disease patients, treated with LLLT on the chest area. In a second study, isolated rat tibial anterior muscles were fatigued with electric current until initial strength was lowered to 50%. Then, the rats were divided into two groups: one treated with LLLT treated and a control group. The laser irradiated group had significantly longer time to reach 50% reduction of strength, significantly higher peak force and significantly lower creatine kinase blood levels (muscle damage index).
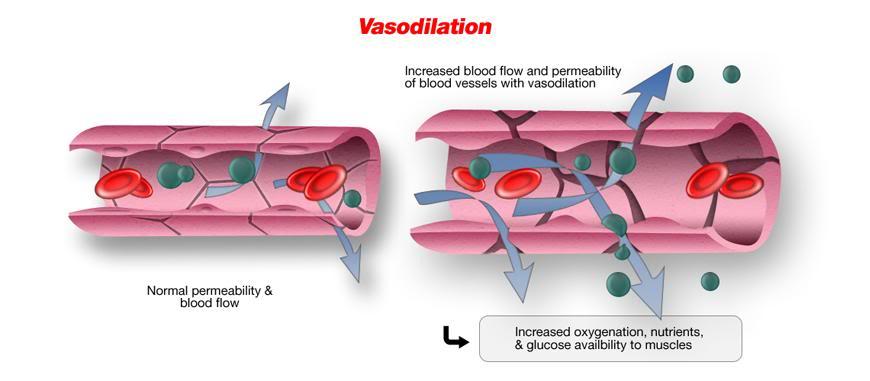
Other studies have shown the important effect of increased blood flow occurring systemically in the body after blood irradiation. A Japanese research group performed LLLT on the common carotid artery area and noted that blood flow volume in the central retinal artery and ophthalmic artery increased. A similar experiment was carried out by Makihara et al, whereby LLLT was applied to the right temporomandibular joint area, which yielded dilation of blood vessels and increases in blood flow volume in the superficial temporal artery.
Surprisingly, this effect was observed bilaterally. Lastly, Wasik et al, observed PO2 and SaO2 increasing after whole blood sample irradiation with 632 nm laser was performed and yet other studies have also reported effects related to increased erythrocyte deformability and microcirculation enhancement.
Mittermayr et al showed that blue laser releases Nitric Oxide (NO) from Haemoglobin (Hb). NO-Hb is a form of met-Hb, with low O2 linking power. Free NO released from Hb is a powerful molecule producing vasodilatation and perfusion enhancement. Concurrently, Hb’s O2 linking power is increased when NO is released. In a study performed by Simonian et al, isolated erythrocyte membranes were irradiated and Citb 558 III activity was measured. Cit b 558 III is a membrane enzyme that restores met-Hb (H+-Hb, CO2-Hb, DPG-Hb) to normal Hb, with higher O2 linking power. Cit b 558 III activity was enhanced after light irradiation.
Once again, I’ll recommend you listen to the podcast “How To Use Low Level Light Therapy And Intranasal Light Therapy For Athletic Performance, Cognitive Enhancement & More” if you want a more detailed explanation of how light irradiation increases blood flow…
…but in simple terms: light is like Viagra for your blood.
Make sense?
OK, now let’s imagine what would happen if we combined light with cold.
—————————
The Effect of Cold (Thermoregulation) on Performance
It’s been shown that both physical and mental functions can be impaired when your body’s core temperature rises and that’s exactly why you’ll see elite athletes dip themselves in “ice baths” or use cold packs not only after an athletic performance, but also to produce performance-enhancing effects during short and intensive resistance exercises and also prior to long endurance events in the heat, such as a cycling stage.
But the issues with these types of aids and treatment with cold is that they don’t penetrate much deeper than skin level.
And worse yet, the cold itself can result in vasoconstriction of the peripheral blood vessels and cause the opposite effect – potentially less blood to working tissue. This type of application of cold does not effective at cooling the body’s core, which includes the main organs and ultimately even the brain.
So it’s a catch-22: yeah, the cold can help keep your core cool and your blood cool. But it also causes a boatload of vasoconstriction.
You know this if you’ve ever taken an ice bath, then tried to go on a run.
Now everyone from Olympic trainers to those in the military Special Forces are always demanding a smarter and more effective way to quickly cool down the body for optimal performance. And luckily, a few researchers at Stanford University have actually successfully demonstrated that heat can be extracted from the body core through the palm of the hand. There are two primary steps involved in cooling the body’s core: convection and conduction of heat from the blood. The Stanford researchers were able to use both heat transfer mechanisms by designing a specialized glove that uses a vacuum to negate the effect that cold has on vasoconstriction.
But unfortunately, as you can see below, the design, weight and size of the “cooling glove” isn’t very practical at all.
———————–
Is There A Way To Enhance Performance By Effectively Combining Light & Cold?
So, we now know photons of concentrated light do some pretty dang cool things to your blood and body.
And we now also know that cold, when used the right way, can be more effective than illegal performance enhancing drugs.
So now we come full circle to the reason I explained all of this to you in the first place: a wearable device called “The Quantlet” that combines light and cold.
See, any of the typical wearable devices on the market right now are designed to measure you vs. doing something to you. This means that many of these new wearables simply measure things like the number of steps you’ve taken, your heart rate or other similar metrics.
But what if you could simply wear a device that actually helped you naturally optimize your own body’s natural physiological functions by leveraging the power of two of Mother Nature’s most powerful yet fundamental forces: light and thermal cooling energy?
Source as always: https://bengreenfieldfitness.com/2016/01/how-to-use-light-and-cold-to-change-your-biology/